star topology. If the workstations are widely dispersed,
the system can use inexpensive hubs with long runs of
shared cable between hubs, similar to the bus topology.
PROTOCOLS
Network protocols are an important component;
they define how networks establish communications
between elements, exchange information, and
terminate communications. Protocols have two major
operational functions. They establish the circuit for
transmission (handshaking) and for the transmission
itself. Transmission is conducted subject to the line
dicipline. The line discipline is the sequence of
operations that actually transmits and receives the data,
handles the error-control procedures, handles the
sequencing of message blocks, and provides for
validation for information received correctly.
Two representative protocols, which control line
dicipline, are: the Binary Synchronous
Communications Protocol (Bisync) and the
Synchronous Data Link Control (SDLC).
and protocol. The principal access methods are
contention and token passing.
Contention
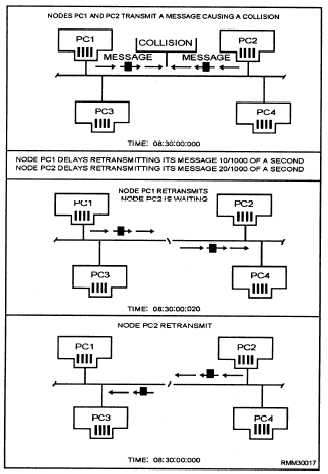
The contention method features Carrier Sense
Multiple Access (CSMA) and Carrier Sense Multiple
Access with Collision Detection (CSMA/CD). (See
figure 1-6.) Access for both is on “a first-come, first-
served basis. The CSMA scheme is very similar to a
citizens band (CB) radio. Stations with data to send
listen to the channel and wait until it is clear to transmit.
With CSMA/CD, if two or more workstations transmit
simultaneously, their messages will collide. As soon as
a workstation detects a collision, it ceases transmission,
monitors the network until it hears no other traffic, and
then retransmits. Most contention networks assign a
unique retry algorithm to vary the wait-and-retry
period. This algorithm reduces the likelihood that after
a collision, two workstations will transmit retries
simultaneously.
l Bisync is a half-duplex protocol that transmits
strings of characters at lower speeds over dial-up
circuits. Information movement is one direction at a
time, with each data transfer being answered by an
acknowledgement.
l SDLC is a control procedure that sends multiple
blocks of data and returns a single acknowledgement
for many blocks, thereby increasing the amount of time
spent transmitting data. The bits that are put before and
after the message at the transmitting end are removed at
the receiving end, so only the message is presented to
the user.
The hardware chosen for the network plays apart in
the choice of network protocol. Most users and many of
the vendors that build clone-type equipment would like
to see universal interfaces. Others feel that the
availability of different specifications will lead to a
proprietary set of equipment, even though they favor the
overall IS0 specifications (which are covered later in
this chapter).
ACCESS METHODS
Another decision to be made is which access
method to use. Access methods are the arrangements
used to ensure that each workstation has fair and equal
access to the network. The access method that will be
used is governed primarily by the network’s topology
Figure 1-6.—A bus network using the CSMA/CD access
method.
1-12